Hypercholesterolemia, commonly called high LDL cholesterol, is the number one, but frequently silent, danger problem for global coronary heart disease and stroke. In our present-day era—wherein way of existence, genetics, and dietary factors intersect—information on hypercholesterolemia is vital for all of us seeking to defend long-term cardiovascular health. This in-depth manual covers hypercholesterolemia’s reasons, warning symptoms, analysis, advanced treatment options, prevention strategies, and solutions to the most frequently asked questions, empowering readers to take informed action.
Table of Contents
What is Hypercholesterolemia?
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Lifestyle Factors
- Medical Conditions and Secondary Causes
- Genetic Forms (Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
- Signs and Symptoms
- Diagnosis and Screening
- Complications and Health Risks
- Treatment Approaches
- Lifestyle Modification
- Medications
- Advanced and Emerging Therapies
- Prevention: Steps for a Cholesterol-Healthy Life
- Living with Hypercholesterolemia
What is Hypercholesterolemia?
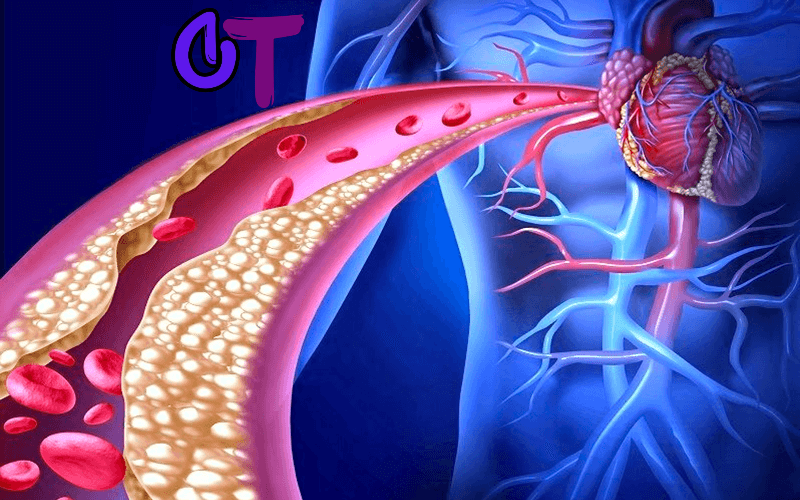
Hypercholesterolemia refers to advanced cholesterol levels in the blood—a biochemical S. Of the us that, at the identical time as regularly silent, dramatically will increase the danger of atherosclerosis (arterial plaque buildup), coronary heart attack, and stroke. Cholesterol is a natural lipid molecule essential for hormone manufacturing, mobile membranes, and bile acid formation. Problems push up at the same time as there may be an increase—mainly of “horrible” LDL cholesterol—that might accumulate inside the arteries and disrupt wholesome blood flow.
Cholesterol travels via the bloodstream in particles referred to as lipoproteins. There are several kinds:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often termed “lousy” LDL cholesterol; excessive degrees cause plaque buildup.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Called “wonderful” LDL cholesterol; carries extra LDL cholesterol away from arteries.
- Very-Low/Intermediate-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL/IDL): Also contribute to LDL cholesterol delivery and threat at the identical time as superior.
Causes and Risk Factors
Lifestyle Factors
Several modifiable elements contribute to the improvement of hypercholesterolemia:
- Unhealthy Diet: High consumption of saturated fats, trans fats, and processed meals will appreciably increase LDL cholesterol. Consuming more red meat, dairy fat, and baked goods at the same time as neglecting fiber-wealthy meals can disrupt LDL cholesterol stability.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary conduct reduces HDL (“proper”) ldl ldl ldl cholesterol and could boom LDL (“awful”) ldl ldl ldl ldl ldl ldl cholesterol.
- Obesity: Extra body fat, in particular in the stomach, can increase LDL cholesterol production.
- Smoking: Lowers HDL at the same time as narrowing blood vessels, hastening plaque formation.
- Excessive Alcohol: Can cause an increase in regular LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Medical Conditions and Secondary Causes
Hypercholesterolemia can also stem from:
Genetic Forms (Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a hereditary contamination affecting about 1 in 250 people globally. It results from gene mutations (typically in LDLR, APOB, PCSK9) that save you the frame from effectively clearing LDL ldl ldl ldl ldl cholesterol, important to dangerously immoderate stages—even in youngsters. FH includes a much better hazard for early coronary heart infection; frequently, lifestyle adjustments on my own aren’t sufficient, and competitive medical treatment is needed.
Signs and Symptoms
Hypercholesterolemia is a “silent” state of affairs—most people reveal no signs and symptoms for years. When levels of cholesterol result in massive artery narrowing or damage, symptoms also can encompass:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Symptoms of coronary heart disorder, coronary heart attack, or stroke
- Rarely, with extreme or inherited office paintings:
- Xanthelasma: Yellow ldl ldl ldl ldl ldl cholesterol deposits on eyelids
- Xanthomas: Cholesterol nodules on tendons, elbows, knees, or arms
- Corneal arcus: A white or grey ring within the course of the cornea.
Diagnosis and Screening
Regular screening for hypercholesterolemia is generally encouraged, specifically for adults over 20 or people with risk factors:
- Lipid Panel (Blood Test): Measures LDL, HDL, total cholesterol, and triglycerides after fasting.
Thresholds:
- LDL ≥ one hundred thirty–160 mg/dL (excessive chance)
- Total LDL cholesterol > two hundred mg/dL is considered borderline to moderate to high.
- Additional Tests: For human beings with family history or as an option, high LDL cholesterol, genetic assessments, or advanced lipid assessment may be required.
Complications and Health Risks
Untreated hypercholesterolemia can result in:
- Atherosclerosis: Hardening and narrowing of arteries because of plaque buildup
- Coronary Artery Disease: The Main cause of coronary heart assaults
- Stroke: Reduced blood flow to the mind
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Blockages in arteries outside the coronary heart
- Early Heart Disease in FH: Heart troubles may additionally arise earlier due to the fact that young adults or 20s in familial times.
Treatment Approaches
Lifestyle Modification
Lifestyle adjustments are the first-line remedy for moderate to moderate hypercholesterolemia:
Diet:
- Reduce saturated and trans fats and processed food.
- Increase fiber (give up, give up, prevent, give up end result, vegetables, whole grains, beans)
- Choose lean proteins (fish, bird, legumes)
- Use plant-based, absolutely oils (olive, canola) in place of butter.
Exercise:
- At least 1/2-hour of mild hobby, 5 days a week
Weight Management:
- Achieve and preserve a healthy frame weight.
Avoid Smoking:
- Quitting boosts HDL and lowers artery risk.
Limit Alcohol:
- Helps prevent triglyceride spikes
Medications
If way of existence measures aren’t sufficient—particularly for humans with FH or higher cardiovascular hazard—tablets are prescribed:
- Statins: Block LDL cholesterol production inside the liver (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin)
- Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors: (e.G., ezetimibe)
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: Monoclonal antibodies that decorate LDL clearance (e.g., alirocumab, evolocumab)
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: Bind ldl ldl ldl ldl ldl cholesterol in the intestine for removal
- Fibrates and Niacin: Mainly lower triglycerides and may help boost HDL
- Bempedoic Acid, Lomitapide, Evinacumab: For immoderate inherited times or those illiberal to statins
- Lipoprotein Apheresis or Liver Transplant: In uncommon, refractory familial instances.
- Note: Therapy is customized to the man or woman’s threat and might include mixtures for maximum impact.
Advanced and Emerging Therapies
- Novel Drug Classes: New injectable and oral medications are in medical use for “tough-to-address” instances
- Gene Therapy: Research is ongoing into techniques to correct genetic errors at the cellular level.
Prevention: Steps for a Cholesterol-Healthy Life
Preventing hypercholesterolemia regularly comes all the way right proper right down to a healthy way of life:
- Maintain a healthful weight loss plan: Low in saturated/trans fats, high in fiber, plant-based, clearly in truth fat.
- Regular exercise: Aerobic and electricity sports sports sports
- Healthy body weight: Avoid overweight/weight problems
- Don’t smoke; limit alcohol.
- Monitor blood pressure and glucose.
- Routine LDL cholesterol screening for early detection.
Living with Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia, even for human beings with inherited office work, may be managed for an extended, healthy lifestyle, as addressed earlier. Most people will need an aggregate of lifestyles and remedies, monitored by their healthcare organisation over the long term. Strategies encompass:
- Regular checkups: Blood checks every 3–12 months, depending on chance/severity
- Medication adherence: Take drug remedies as prescribed
- Adapted manner of life: Make coronary heart-healthy eating and exercise a habit.
Conclusion
Hypercholesterolemia is a silent, however tractable stress within the realm of cardiovascular contamination—the region’s big variety-one killer. Through a combination of a healthy eating plan, workout, knowledgeable screening, and suitable scientific treatment, it’s possible to maintain LDL cholesterol in check and enjoy a prolonged, healthier lifestyle. Know your numbers, understand your chance, and work hand-in-hand on the component of your healthcare business enterprise to create an LDL cholesterol-reducing plan that works for you.
(FAQs)
What’s the difference between hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia?
A: Hypercholesterolemia refers especially to excessive LDL cholesterol, usually LDL. Hyperlipidemia covers all blood lipids, which include LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Can I experience if I clearly have immoderate LDL cholesterol?
A: No—maximum humans are symptom-free till immoderate artery sickness develops. Regular blood assessments are important for detection.
Is it continuous because of the horrible manner of lifestyles?
A: Not continuously. Familial hypercholesterolemia is inherited and may require a medicinal drug from an early age, despite the fact the lifestyle is healthy.
Which food do need to I keep away from?
A: Limit red meats, whole-fat dairy, butter, baked gadgets made with shortening, fried components, and processed snacks high in trans or saturated fats.
How regularly ought to I take a look at my ldl ldl ldl ldl ldl cholesterol?
A: Adults over 20: every four–6 years if low threat; extra often when you have danger elements or your own family facts. Those on treatment or with heart danger: every 3, one year ordinary with a medical clinical doctor’s recommendation.